Making News
Assessing Health of Our Young Ones: HBYC Periodic Assessments in Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan
The Government of India implemented Home Based care for Young Child (HBYC) program in 2018. HBYC is designed and built on the architecture and experience of the Home Based Newborn Care Plus (HBNC+) program which NIPI introduced and piloted in 13 districts of four states Rajasthan, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh and Bihar. HBYC is an intervention package addressing the survival and development of every young child in the community. The program is being implemented in aspirational and non-aspirational districts of five NIPI focus states including Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan since 2019. NIPI provides techno-managerial support for its effective implementation.
.jpg)
.jpg)
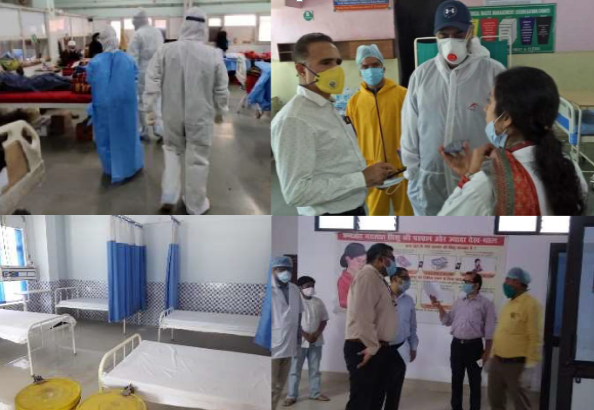
The states of Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan planned and undertook periodic assessment of HBYC program in their respective state. This vast and important exercise was conducted in eight aspirational districts of Madhya Pradesh (Rajgarh, Guna, Damoh, Chhatarpur, Badwani, Khandwa, Singrauli and Vidisha) and five aspirational districts in Rajasthan (Baran, Dhaulpur, Jaisalmer, Karauli and Sirohi). The state of Rajasthan expanded the mandate of the assessment by further including another 15 non-aspirational districts as well. The objectives of the assessment were: 1) to ascertain the implementation of the HBYC program implementation status, 2) to assess knowledge and practices of field functionaries (ASHA, ANM, AWW and ASHA supervisors) as well as the mothers of young children (the beneficiaries) being visited under HBYC. These assessments in both states were supported by the NIPI team and jointly conducted with team members from the state NHM. NIPI supported both states in developing and finalizing the methodology, sampling techniques, data collection tools including an APP using the DHIS2 platform.
Prior to the actual visits and data collection in the field, an orientation of the assessment team members on the scope of the assessment and relevant tools was organized in both states. The assessment was conducted in Madhya Pradesh from 3-19th February and in Rajasthan from 15-26th March, 2021. During the assessments in both states, more than 2,800 ASHAs, 2,700 Mothers and 700 other health workers were interviewed. Interviews with state and district programme managers from the selected 28 districts in both states were also conducted to assess the preparedness of the health system in implementation of HBYC.
.jpg)
Following the completion of assessments, the data was analysed and findings were compiled. NIPI shared the results and findings of the assessment with key NHM officials and other stakeholders in meetings organized by both states. These meetings also served as an opportunity to share the challenges and gaps in the implementation of HBYC in both Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan. These meetings were chaired by state NHM officials from Child Health and ASHA divisions. Both state Governments have acknowledged and valued the technical support provided by NIPI during these assessments and ensured corrective measures to further strengthen implementation of the HBYC program in their respective state.
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)







.png)